NASA agency James Webb Space Telescope Getting ready for a deep space chemistry experiment.
During the commissioning of the observatory and continuous mirror alignmentWebb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) team has successfully completed an initial examination and characterized three primary mechanisms for the device to do its job.
Several NIRSpec representatives wrote in Webb’s blog post Thursday (March 3).
Live updates: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope mission
Related: How does the James Webb Space Telescope work?
Once turned on, NIRSpec will split light From targets Webb observes to what scientists call spectrographs, they measure the amount of light at specific wavelengths. These fingerprints can teach astronomers about galaxies, exoplanets and other objects, highlighting properties such as mass, temperature and chemical composition.
Using NIRSpec, Webb can capture spectra of up to 100 galaxies At the same time, making observations more efficient since collecting photons of light from such distant objects would take the observatory hundreds of hours.
The Webb blog post mentioned that the three main mechanisms of the NIRSpec are the filter wheel assembly, the grooved wheel assembly, and the refocusing mechanism assembly.
Here’s how the instrument works: A grooved wheel spreads light from a target of interest into its colors (wavelengths) to create a spectrum. The filter wheel reduces pollution by blocking wavelengths outside of what scientists are interested in. Then the refocusing mechanism adjusts and sharpens the NIRSpec focus.
Engineers checked each of these assemblies separately, starting with the filter wheel assembly to ensure that its eight positions in the forward and reverse directions were working.
“At each site, we recorded a set of reference data,” NIRSpec officials wrote. “This data showed us how well the wheel moved, and how accurately it settled in each position. Between each…position, we downloaded ‘High Capacity Buffer’ data from the positioning sensors, and the NIRSpec team analyzed the data. The data showed that the wheel moved steadily. Very good even on the first try.”
Then, Webb engineers recorded the reference data for the mesh wheel assembly and rotated the positions in roughly the same way, showing that everything was working correctly.
Then with the refocusing mechanism (RMA) assembled, engineers also collected raw data before ordering the mechanism to move forward “a few hundred steps from launch position,” the blog post states.
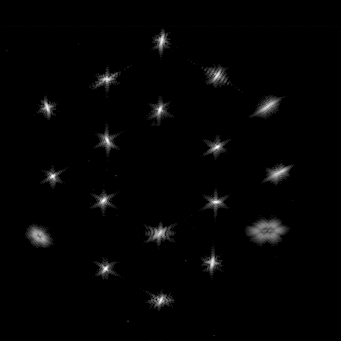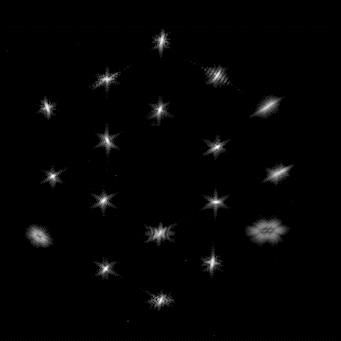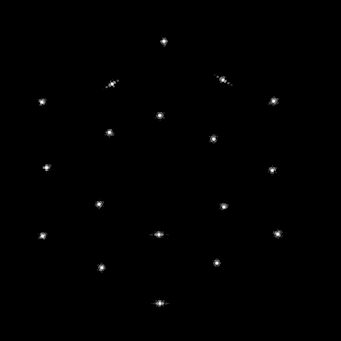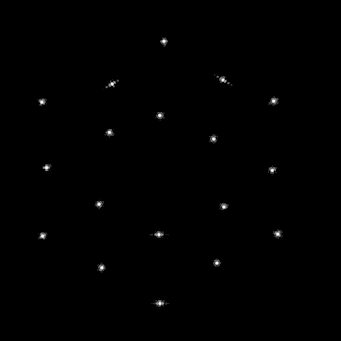
In the blog post, the NIRSpec team added, “After the initial step, we commanded the RMA mirrors to their previous best focus position. Successful completions of this test showed us that the RMA is a well-behaved and healthy mechanism.”
In the middle of the tool dragging, the Webb mirror alignment continues in its fourth stage, focusing on a “rough gradient” that measures and corrects small height differences between individual mirror segments, the blog noted. The telescope is still in excellent health after its December 25 launch and has enough fuel for at least 20 years of operation.
Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter Tweet embed. Follow us on Twitter Tweet embed and on Facebook.

“Infuriatingly humble analyst. Bacon maven. Proud food specialist. Certified reader. Avid writer. Zombie advocate. Incurable problem solver.”
